Stroke has 2 forms: due to brain bleeding or cerebral ischemia, regardless of the cause, any stroke has many consequences for patients because most patients often have diseases (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular,...).
The initial symptoms of a stroke appear suddenly. Symptoms depend on the location of the infarction (see Figure Areas of the brain by function).
Symptoms include numbness, weakness of the extremities and face, aphasia, confusion, visual disturbances in one or both eyes, dizziness or loss of balance, headache.
Both hemorrhagic stroke or ischemic stroke have the severe consequence of damaging an area of the brain parenchyma, the extent of the damage depends on cerebral blood flow and how long the brain has been damaged. If the brain suffers major damage, then the nerve cells lose their function permanently, so a stroke requires timely treatment and the right method to shrink the damaged area of the brain.
Heart-related complications, pneumonia, venous congestion, fever, pain, difficulty swallowing, limb spasticity, depression,... are all common complications of the disease. Complications of stroke and stroke cause patients to suffer severe health and psychological effects, which can lead to temporary disability or permanent disability.
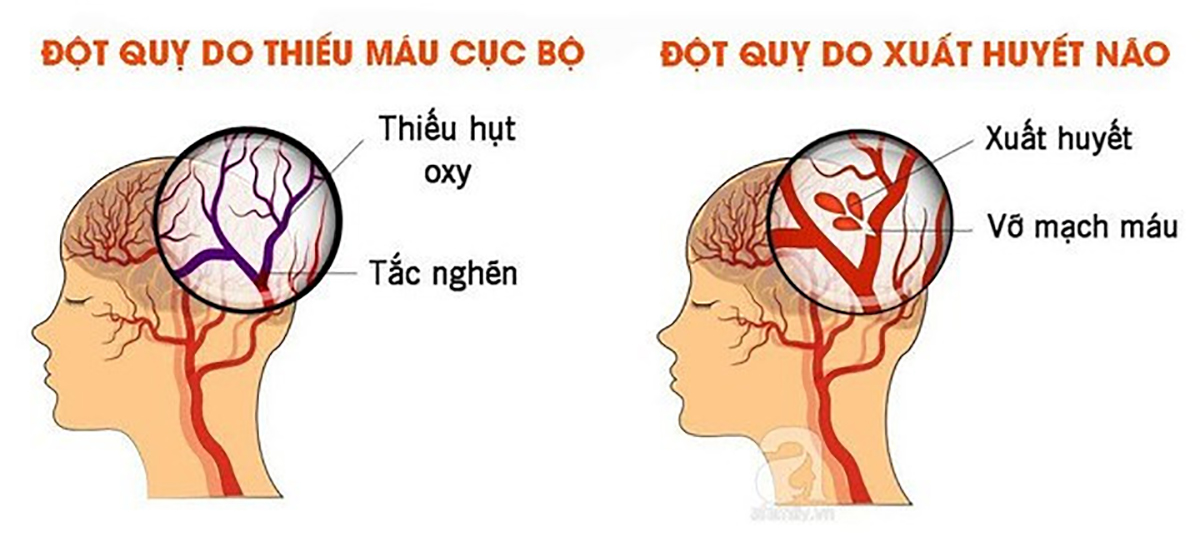
Complications in which location depends on where the brain is affected and how long the brain is without oxygen include:
- Brain edema after stroke.
- Pneumonia: stroke patients with cerebrovascular accident often have difficulty swallowing, thereby leading to the phenomenon of food and drink easily entering the lungs causing pneumonia.
- Heart attack: 1/2 of strokes are associated with atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attack after stroke due to the existence of atheromatous plaques.
Depression: It can get worse for patients who have been depressed before a stroke.
- Pressure ulcers (prolonged bedridden time): People who have a stroke often lose mobility, have to lie or sit still for a long time, causing ulcers.
Epilepsy: After a stroke, the brain may have abnormal activity, causing seizures.
Visual disturbances: People who have had a stroke may experience reduced or lost vision in 1 or both eyes.
- Limb spasticity: Loss of mobility, weakness or paralysis of one hand.
- Thrombosis: Loss of mobility or limited mobility causes blood clots to form in leg veins.
- Urinary tract infections (occur in stroke patients with foley catheterization).
- Decreased cognition (memory loss).
- Loss of speech function, difficulty speaking, incomplete speech, talking nonsense, not understanding what others say...
What should be done to prevent stroke?
- Do not smoke, do not drink alcohol.
- Eat according to a scientifically sound diet.
- Increase physical fitness.
- Avoid stress.
- Early detection, timely treatment and stable control of underlying diseases: diabetes, cardiovascular, blood pressure,...
See more product information here.