Acute conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is a common ocular condition. The disease is quite benign, when cured, it leaves few sequelae but is very contagious, can become large outbreaks, especially in crowded places such as schools, hospitals, offices, swimming pools ... affecting the ability to work, study and live.
The disease thrives in summer due to the hot and humid climate, lots of smog and pollution that are favorable factors for pathogens.
Causes of pink eye
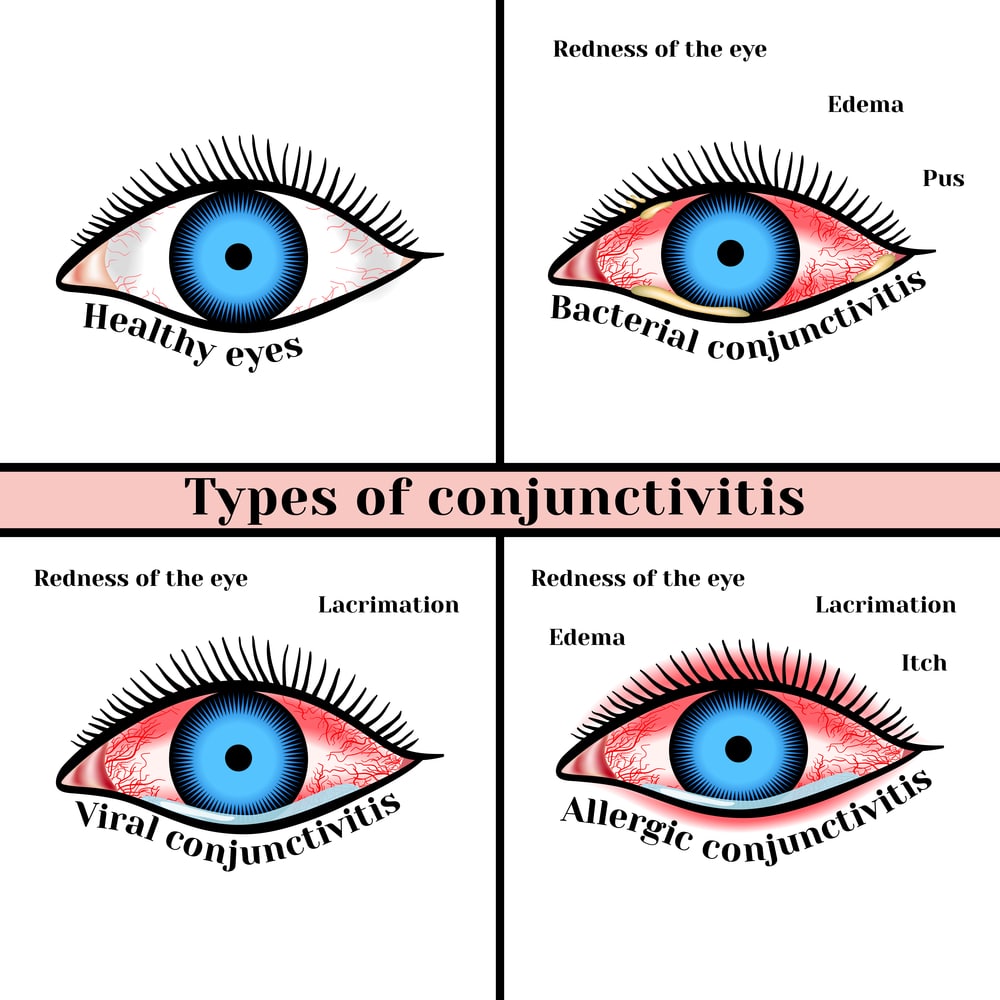
There are 4 main pathogens, including bacterial, viral, allergic and papillary conjunctivitis caused by contact lenses.
Specifically, many types of bacteria can cause acute conjunctivitis such as pneumococcus, staphylococcus, streptococcus, gonorrhea, diphtheria ... In newborns may develop gonococcal conjunctivitis through the genital tract of a mother with gonorrhea.
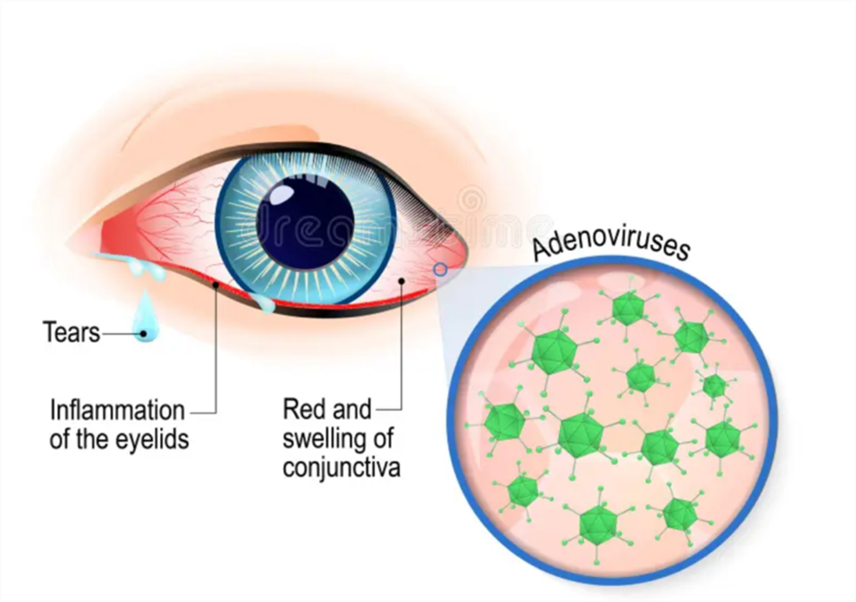
The most common pathogenic virus is Adenovirus, which often spreads strongly causing large outbreaks (lymph throat conjunctivitis) due to its respiratory characteristics and ability to survive for a long time in the environment. There are also Enteroviruses, Herpes viruses ...
Patients in contact with allergens lead to rapid redness of the eyes, itching a lot, making the patient rub their hands over the eyes, and is the cause of superinfection, may also have itching, runny nose. The disease often recurs intermittently, persistent white hormones, sometimes yellow hormones, sensitivity to light, blurred vision. Treatment should be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
In addition, pink eye is caused by giant papillary conjunctivitis, associated with long-term use of contact lenses.
Symptoms of pink eye
After the incubation period (counting from contact with the infectious source) 2-3 days will appear signs of itchy eyes, redness, glare, photophobia, tearing and a lot of discharge in the eyes. If you wake up many mornings and make the eyelashes stick together, it is difficult for the patient to open his eyes. Alum also makes the patient find vision difficult and entangled, but the vision usually does not decrease.
On eye examination, red swollen eyelids, erect conjunctiva, edema. Multiple alum on the eyelashes and conjunctival surface. In some cases there may be hemorrhages (bleeding) under the conjunctiva. If the cause of the disease is streptococcus, pneumococcus, diphtheria ... then the ciliary conjunctiva is usually covered with pseudomembranous.
Severe cases can cause corneal damage such as superficial dotted keratitis, spotted keratitis that causes the cornea to become opaque, when vision is much reduced and persists for months. If the cause is adenovirus, then the person may have a low-grade fever, runny nose, swollen lymph nodes in front of the ear or angular nodes of the jaw, pharyngitis, swollen tonsils.
How is the treatment?
Patients with conjunctivitis should go to ophthalmological facilities for diagnosis and advice on appropriate treatment. Also, avoid using tobacco to apply or fumigate your eyes as not only have little therapeutic effect but can also cause other damage to the eyes such as heat burns or essential oils.
Some species of fungi and bacteria in the leaves of plants can penetrate through corneal scratches, causing a very dangerous pathology, corneal ulcers. At that time, the treatment will be extremely difficult and expensive and the sequelae left behind are corneal scars that cause permanent open vision, in some severe cases, the eye must be removed.
Acute conjunctivitis rarely requires parenteral antibiotics. Usually doctors only prescribe antibiotic eye drops 5-7 times per day. Washing the eyes with physiological mosquito water NaCl 0.9% many times, the effect of washing away the eyes and pathogens helps to recover quickly. Use artificial tear drops 4-6 times daily to reduce discomfort.

See more product information
here.