Vildagliptin is a type 2 diabetes medication, DPP-4 (Dipeptidyl peptidase - 4) inhibitor group, also known as gliptin group, helps control blood sugar and HbA1C, the binding index of sugar on Hb (hemoglobin) of red blood cells. However, the medicine has side effects that need special attention when using.
Improves blood sugar control
After eating, blood sugar rises, the digestive mucosa secretes incretin, also known as GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide 1), which has the function of regulating, increasing insulin secretion, and reducing blood sugar after eating. Meanwhile, enzyme DPP-4 inhibitors GLP-1, inactivating insulin secretion, causing blood sugar to rise.
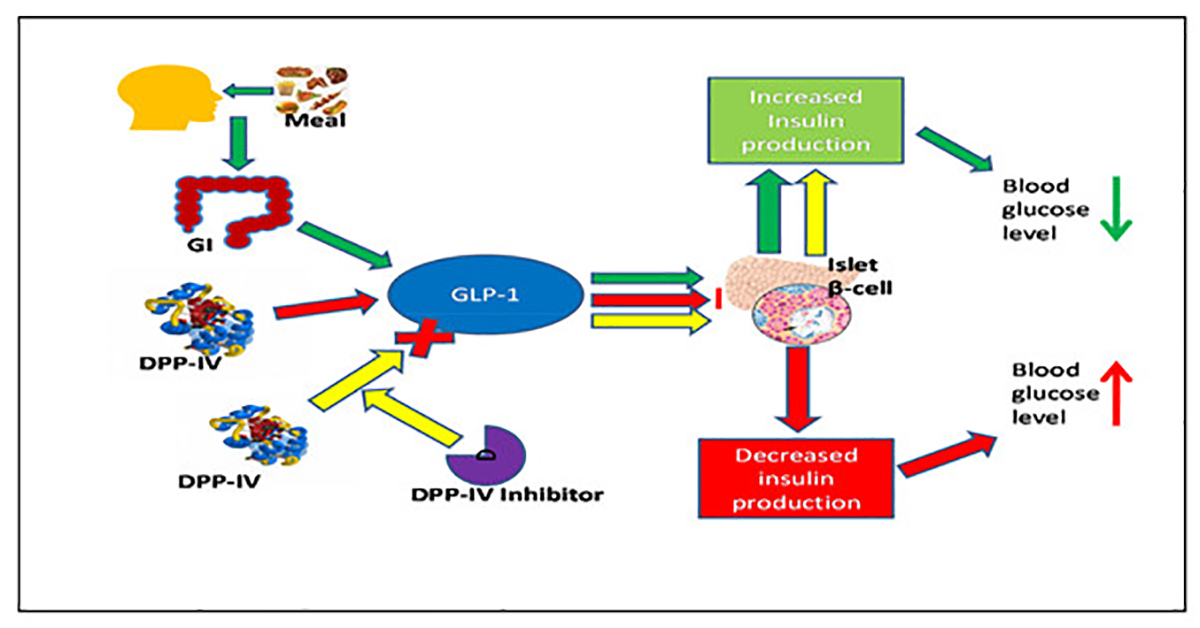
New generation type 2 diabetes drugs have similar effects to GLP-1, inhibiting DPP-4 enzyme to reduce postprandial blood sugar. Vildagliptin is a member of this class that selectively inhibits DPP-4, which improves glycemic control and HbA1C.
By increasing endogenous concentrations of incretin hormones, vildagliptin enhances the sensitivity of beta cells to glucose, leading to improved glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with doses of Vildagliptin 50 - 100 mg daily resulted in significant improvements in beta-cell function. In people without diabetes (normal blood sugar), Vildagliptin does not stimulate insulin secretion or cause a decrease in glucose levels.
Cases requiring special attention
Vildagliptin has an important advantage, which is to reduce blood sugar after eating without causing excessive hypoglycemia, which is very convenient for the elderly or people with long-standing diabetes. However, Vildagliptin is not indicated as a substitute for insulin in patients requiring insulin. Vildagliptin must not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
For people with liver failure: Cases of liver dysfunction (including hepatitis) should be used with caution when using this drug. Discontinue treatment with Vildagliptin if AST or ALT rises to 3 times the upper limit of normal. During treatment, liver function tests should be checked every 3 months and periodically thereafter. Discontinue use if the patient develops jaundice or other manifestations suggestive of liver dysfunction.
Renal Impairment: No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment. In patients with severe, moderate renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) the recommended dose of Vildagliptin is 50 mg once daily. However, it should be used with caution in these end-stage patients.
Acute pancreatitis: Vildagliptin use increases the risk of acute pancreatitis. Patients should be informed of the characteristic symptoms. If pancreatitis is suspected, use should be discontinued.
Pregnancy and lactating women: There are insufficient data on the use of Vildagliptin, and potential human risks have not been established. However, animal studies have demonstrated reproductive toxicity at high doses, and Vildagliptin is also excreted in milk. Therefore, this medicine should not be used during pregnancy and lactating women.
Source: Health and Life Newspaper

See more product information here.