Helicobacter pylori (H.p) bacteria have long been found to live in the mucus layer adjacent to the gastric mucosal epithelium. 60-90% of peptic ulcers are caused by H.p. Since 2005 the World Health Organization has officially classified H.p as the cause of stomach cancer. Helicobacter pylori also causes a number of other diseases in the stomach such as functional dyspepsia. In addition, H.p also causes diseases outside the digestive organs: such as primary thrombocytopenia.
METHODS OF DIAGNOSING H.P INFECTION
- Rapid urease test: During endoscopy, sensitivity > 98% and specificity 99%.
- Breathing test: Using C13 radiocarbon, sensitivity 95% and specificity 96%.
- Cultivation.
- Histopathology: Sensitivity > 95% and specificity > 95%.
Anti-Hp antibodies in serum.
- Test for H.p antigen in stool.
- In clinical practice, only rapid urease test and breathing test are used to diagnose and monitor treatment of H.p. Bacterial cultures are used to make antibiograms in cases of antibiotic resistance.
TREATMENT
a) Principle
- It is mandatory to do the H.p test first.
- Use oral antibiotics, not injectable antibiotics.
- Must be treated in combination with acid-reducing drugs with at least two antibiotics.
- Do not use a single antibiotic.

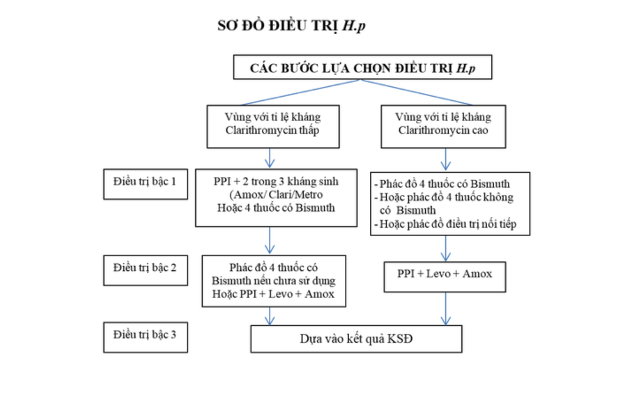
b) First choice regimen
Only where clarithromycin resistance is < 20%. When taking 14 days more effective than 7 days:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) x 2 times/day and 2 of 3 antibiotics:
+ Clarithromycin 500 mg x 2 times/day.
+ Amoxicillin 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
+ Metronidazole 500 mg x 2 times/day.
c) Regimen of 4 alternative drugs
When there is antibiotic resistance or in areas where the rate of clarithromycin resistance is over 20%, 14-day use includes:
+ Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) x 2 times/day.
+ Colloidal bismuth subsalicylate/subcitrate 120 mg x 4 times/day.
+ Or replace PPI + bismuth with RBC (ranitidine bismuth citrate).
+ Metronidazole 500 mg x 2 times/day.
+ Tetracycline 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
If Bismuth is not available, the next regimen or regimen of 3 antibiotics can be used:
- Four-antibiotic regimen for 14 days:
+ PPI x 2 times/day.
+ Clarithromycin 500 mg x 2 times/day.
+ Amoxicillin 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
+ Metronidazole 500 mg x 2 times/day.
- The next outline:
+ 5-7 days: PPI x 2 times/day + amoxicillin 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
+ 5-7 days followed: PPI x 2 times/day + clarithromycin 500 mg x 2 times/day + metronidazole or tinidazole 500 mg x 2 times/day.
In case H.p is still resistant to drugs, an alternative regimen can be used after 14 days of use:
- 3-drug regimen with Levofloxacin:
+ PPI x 2 times/day.
+ Levofloxacin 500 mg x 1 time/day.
+ Amoxicillin 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
4-drug regimen with Levofloxacin:
+ PPI x 2 times/day.
+ Levofloxacin 500 mg x 1 time/day.
+ Bismuth x 4 times/day.
+ Amoxicillin 1000 mg x 2 times/day.
d) In case the above regimens are not effective, it is necessary to culture bacteria and make an antibiotic chart.
Source:
1. Guidelines for the use of antibiotics Ministry of Health (2015) Eradicating Helicobacter pylori in gastroduodenal disease page 145-147.
2. Vietnam Association of Gastroenterology (2013), Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori in Vietnam, Medical Publishing House.
3. Treatment protocol of Cho Ray Hospital and Gia Dinh People's Hospital.
4. Acid secretion of gastric juice and related diseases Assoc. Prof.Dr. Dao Van Long, Medical Publishing House 2014.
5. Link: http://soyte.sonla.gov.vn/67/1051/2079/537739/thong-tin-y-hoc/phac-do-dieu-tri-vi-khuan-hp-da-day-moi-nhat-cua-bo-y-te
