According to the Vietnam Endocrinology and Diabetes Association, there are about 5 million people with diabetes in the country, of which type 2 diabetes accounts for 90%-95%. Every day at least 80 people die from related complications. Diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, often doesn't show symptoms until it's advanced. If not detected and treated in time, diabetes patients will be prone to extremely dangerous complications.
Chronic complications
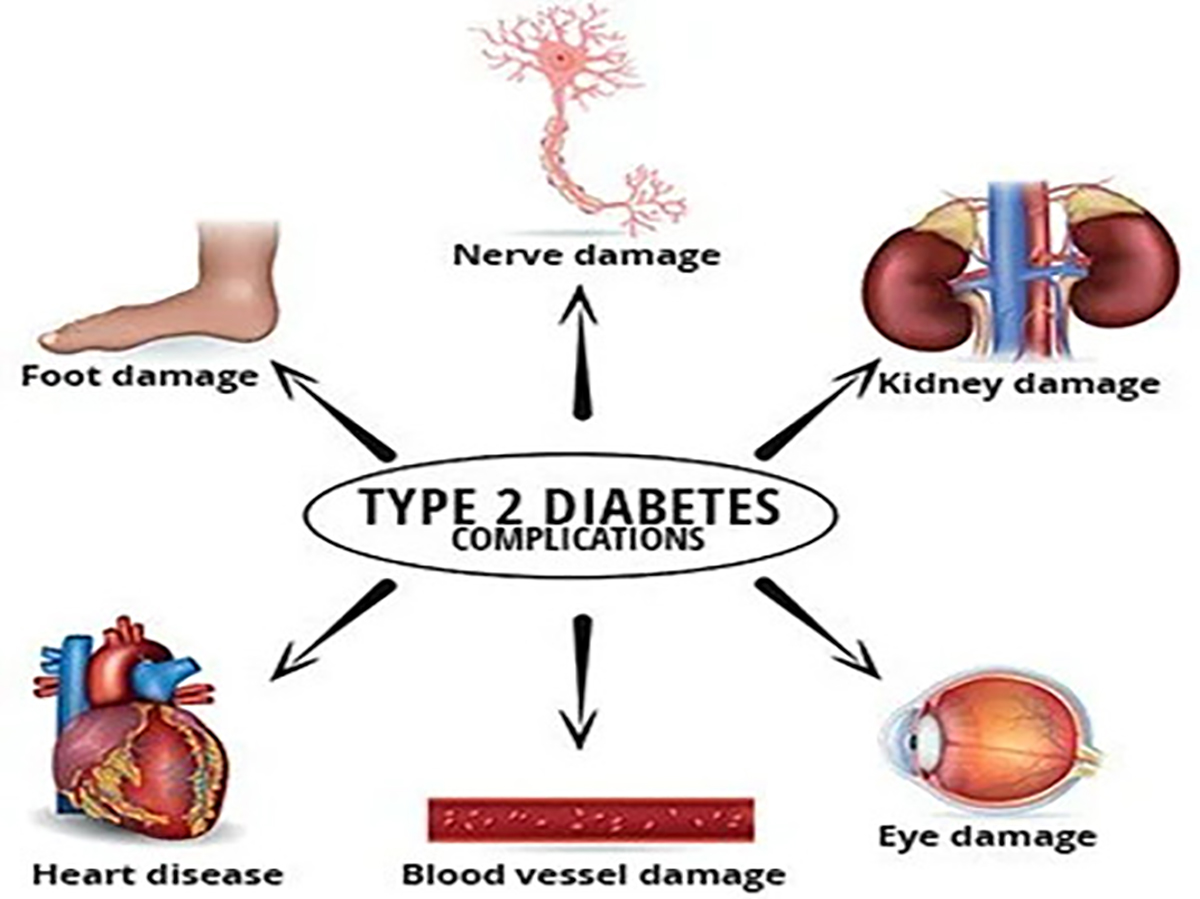
Cardiovascular complications: Diabetes increases the risk of high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident causing paralysis or death.
Kidney complications: Diabetes causes damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys that lead to kidney failure or kidney failure. Kidney disease is more common in people with diabetes than in people without. Maintaining normal blood glucose levels and blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of kidney disease.
Nerve complications: Nerve damage is a common complication and often appears early in people with diabetes. Type 2 diabetes can cause nerve damage throughout the body when blood glucose and blood pressure are too high. Manifestations such as: numbness, loss of sensation or sensory disturbances, muscle atrophy, pain, drooping eyelids, strabismus, facial paralysis... Damage to the autonomic nerves can also cause myocardial infarction, bladder paralysis, paralysis positive, digestive disorders...
Vision complications: Most people with diabetes will develop some type of eye disease that reduces vision or goes blind. Persistently high blood glucose levels along with elevated blood pressure and high cholesterol are the main causes of retinopathy. This condition can be controlled through regular eye exams, keeping blood glucose levels and blood pressure near or normal.
Risk of infection: High blood sugar is a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, and at the same time weakens the body's immune system, so it is easy to get infections such as dental, urinary or genital infections. long-lasting sores... Inflammation is often long-lasting, persistent and difficult to treat.
Complications during pregnancy: High blood glucose during pregnancy can lead to an overweight baby. This easily leads to obstetric complications for children and mothers; the risk of sudden hypoglycemia in the newborn baby; Children exposed to high blood glucose during pregnancy have a higher risk of developing diabetes in the future than other children.
In addition to the above complications, high blood sugar can also damage many other organs of the body such as bones, joints, brain, memory loss or skin diseases...
Acute complications
Hypoglycemia: occurs when blood sugar falls below 3.6mmol/l. Causes can be an overdose of blood sugar-lowering drugs, eating too much or not eating but still taking drugs, exercising too much or drinking too much alcohol. The patient's signs are hunger, fatigue, tremors in the limbs, weakness, sweating, dizziness, nervous palpitations. If not treated promptly, it can lead to coma or even death.
Coma: Too high blood sugar can cause coma due to increased osmotic pressure, this is the most serious and very fatal complication that requires the patient to be treated immediately.Ketoacidosis: A toxic state in which the blood is acidic due to increased acidity, this is the result of incomplete metabolism caused by insulin deficiency. The patient can die if not treated promptly.
Diabetes is a long-term chronic disease, patients have to live with the disease for the rest of their lives. Although diabetes cannot be cured, it can be completely controlled if the patient knows how to take care of their health along with proper treatment as directed by the doctor.
Source: Nam Dinh Department of Health

See more product information here.