Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia due to impaired insulin secretion or insulin resistance. Early symptoms include: drinking a lot, thirsting a lot, urinating a lot, and losing a lot of weight. Uncontrolled prolonged hyperglycemia will lead to acute and chronic diabetes complications, causing damage to many different organs such as the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Diabetes
1. Dangerous complications of diabetes
1.1 Acute complications
- Hypoglycemia
When blood sugar levels are below 70 mg/dL (4.2 mmol/L) , people with diabetes may experience signs such as sweating, chills, increased heart rate, and extreme hunger. , weak limbs, blurred vision or impaired vision.
The cause of this acute complication of diabetes is largely related to the use of drugs, insulin and irregular lifestyle (drinking a lot of alcohol, skipping meals, exercising a lot without supplementing enough energy). quantity,...).
- Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is the most dangerous acute complication of type 1 diabetes. Due to the body's lack of insulin, fat must be broken down to create energy for the body to function. The resulting accumulation of ketones in the blood gradually develops into ketoacidosis.
Signs of recognition include: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity breath (the smell of ketones), frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, confusion, and deep breathing.
- Increased osmotic pressure
Increased blood osmotic pressure, also known as HHS (Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome) . This complication occurs when blood sugar levels are too high for a long time, drawing water from organ cells, leading to severe dehydration.
Warning signs of HHS in diabetic patients include: dry mouth, excessive thirst, confusion, always feeling sleepy, hallucinations, nausea, physical weakness,...
1.2 Chronic complications
are complications that develop silently for many years, but will leave great consequences, greatly affecting the patient's health. Chronic complications of diabetes include macrovascular complications and microvascular complications.
Macrovascular complications
Macrovascular complications of diabetes are atherosclerosis with clinical consequences:
- Stroke due to cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, especially lacunar cerebral infarction. Sometimes patients experience a transient ischemic attack (TIA).
- Myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction.
- Peripheral vascular disease causes limb embolism and limb necrosis.
Microvascular complications
Microvascular complications cause damage to a number of organs such as the eyes, kidneys and nerves:
- Eye complications
High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and cause eye complications such as retinopathy, small vascular hemorrhages in the fundus, cataracts, glaucoma, decreased vision or can lead to blind. Therefore, people with diabetes need to have regular eye exams (every 6-12 months) to detect early signs of eye abnormalities for treatment and prevention.
- Kidney complications
High blood sugar damages the microblood vessels in the kidneys, thereby reducing the kidney's filtering function, causing kidney failure. Symptoms of diabetics experiencing kidney complications include: increased blood pressure, edema, insomnia, fatigue, loss of appetite, etc. To prevent these complications, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle and control sugar. blood and periodically screen for kidney complications.
- Neurological complications Neurological
complications occur due to increased blood sugar, causing damage to blood vessels that feed the nerves, causing loss of feeling in the legs and arms. More seriously, neurological complications can cause people with diabetes to not be able to feel danger signs in their feet, risking foot ulcers. Foot injuries, if not well controlled, will lead to the risk of amputation or even death due to blood vessel blockage.
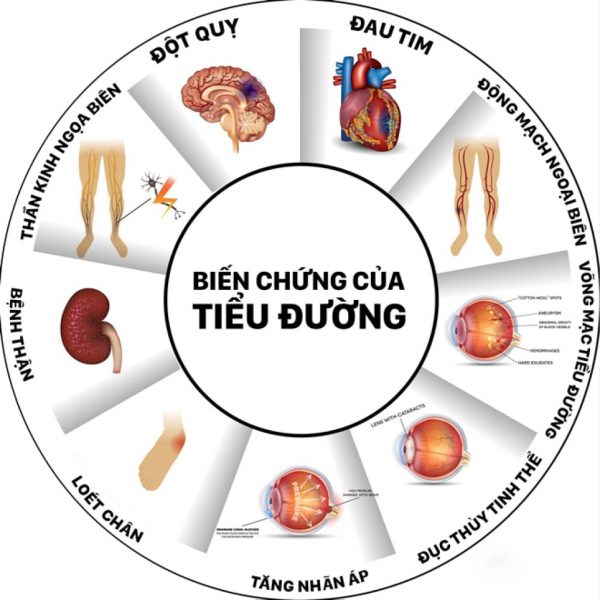
Complications of diabetes
2. Some measures to diagnose diabetes complications
To detect early and limit complications of diabetes, we should have regular health checks and perform clinical and paraclinical examinations. Follow your doctor's instructions to be able to screen for complications well
- HbA1C test: blood test used to check the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- FPG test (fasting plasma glucose): Patients need to fast for at least 8 hours to perform the test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: measures the body's ability to use glucose.
- Random plasma glucose testing.
3. Blood sugar control methods help prevent complications of diabetes
- Compliance with medication use: People with diabetes need to take medication as recommended by their doctor, ensuring enough medication, enough dosage and enough time. In addition, regular follow-up examinations should be performed every 1-3 months depending on the disease condition to check diabetes status, evaluate the effectiveness of the drug and consider changing the dosage if necessary.
- Control your diet: Special attention should be paid to controlling your diet to avoid sudden increases in blood sugar. People with diabetes should cut down on the amount of starch in white rice, wheat, potatoes, cane sugar, lactose, etc. Limit salt and bad fats (animal fats, fats in processed foods). , protein from red meat, eggs, milk. Instead, you should eat lots of fruits and vegetables and foods rich in soluble fiber in steamed or boiled form to limit fat. Meals should be divided into smaller portions throughout the day, alternating snacks with fruits that do not increase blood sugar such as mango, grapefruit, orange, dragon fruit, strawberry...
See more products here